Infection Control: Hand Washing

Disease
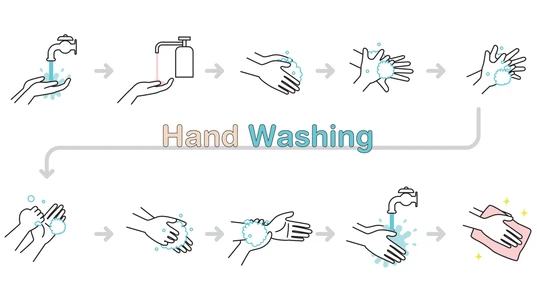
Hand washing is like a do-it-yourself vaccine for a range of illnesses, including seasonal viruses like the flu and common cold. However, not many people understand handwashing basics, like whether to use regular or antibacterial soap.
You may already know that keeping your hands clean is one of the best ways to prevent a bunch of illnesses, but there is a lot more to keeping your mitts germ-free than you may think. A good old hand washing, with soap and running warm water, is the most effective form of infection control we have. With colds, flus and other seasonal viruses and bacteria eluding us, Australia Wide First Aid thought we would remind you about what it takes to really keep your hands germ-free. Hand washing is like a "do-it-yourself" vaccine for a range of illnesses. Research shows that compared to non-hand washers, those who wash their hands four times a day can have up to 24 per cent fewer sick days due to respiratory infections. Likewise, they can have up to 51 per cent fewer days off due to tummy or gastro viruses. Not only that, it has been said that effective hand washing has the potential to eliminate half of all cases of food-borne illnesses.Here is how you can brush up on your hand washing basics
Don't Rush - A quick splash under cold running water isn't enough. To get germ free, you will need to rub your hands together under clean, running water for 40 to 60 seconds, including the drying. Don't know how to time 40 to 60 seconds? Try singing the "Happy Birthday" song twice. Soap Up - If there is soap nearby, use it. Any germs on your hands will be attached to the layer of acidic fats, oils and cellular debris on the surface of the skin. Using soap will help free the germs. Antibacterial Soap - To ensure you get rid of all the nasties, it may be tempting to use antibacterial soaps. However, there is no proof these products work any better than regular soap and water. Rather, there are fears that these antibacterial products may actually cause harm by encouraging bacteria to become resistant to their active ingredients. Running Water - It is better to use running water, as clean hands are likely to become contaminated again if you wash them in a sink of bowl or water. Temperature Debate - Very hot water may kill disease-causing microbes, but the temperature needed (80degreesC) would leave you with significant burns. Soap lathers better in warm water, which is also less likely to strip away the natural oils in your skin than either hot or cold water. The point to remember is "it is totally impossible to kill the bacteria on your skin only via the temperature of the water you use to wash your hands". No Water - A bottle of alcohol-based sanitiser or gel in your bag can be useful if you need to clean your hands and you can't access water; for example, when you're out and about and need clean hands to eat food. Australia Wide First Aid recommends you choose a product with at least 60% alcohol, which kills germs by direct contact with the alcohol. Drying Matters - commercial hand dryers work well, but paper or cloth towels are best used at home or in work environments. Drying your hands is just as important as washing. Don't Touch - Even if your hands are filthy, if you keep them away from your face (or food) the germs will find it harder to make their way inside your body. Germs can be easily transferred and readily enter cells through our mouth, eyes or ears, making us sick.
Aside from washing your hands thoroughly, you can minimise the spread of infection at the home and workplace by using sanitisers regularly, using an alcohol spray to clean your office space, and coughing or sneezing discreetly and away from others.
Once your hand washing technique is mastered
Make sure you take control of other ways infection is easily spread through your home or workplace.- Wash your hands thoroughly using soap and water within 20 seconds after using the toilet, before preparing food and after touching shared equipment. Dry your hands thoroughly with paper towel.
- Use hand sanitiser regularly to avoid the spread of infection.
- Using an alcohol wipe or spray that is at least 60% alcohol, wipe down your desk, phone and keyboard.
- Cough or sneeze into a tissue or your inner elbow, covering your nose and mouth.
- Use and dispose of tissue appropriately
Originally published at
https://www.australiawidefirstaid.com.au/resources/infection-control
as part of the Australia Wide First Aid Articles Library